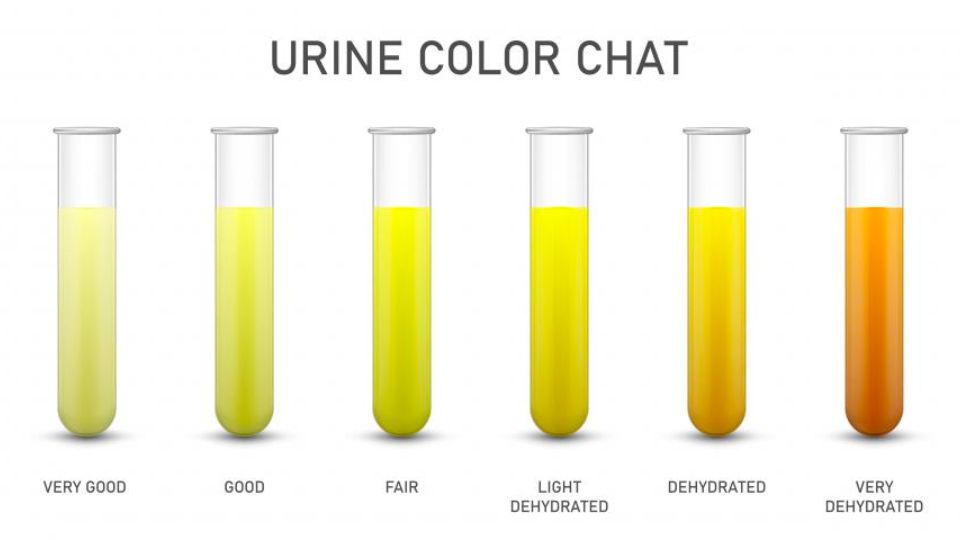
Scientists have long understood the reason behind the yellow color of urine in healthy, well-hydrated individuals. Urobilinogen, a by-product produced by the body as it eliminates 5 million dead red blood cells per second, is responsible for the color. A fascinating puzzle lies in identifying the microorganisms residing in our digestive system that play a crucial role in converting harmful substances into the yellow pigment that colors our urine, all the while maintaining the balance of our blood chemistry.
A groundbreaking study was recently published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Microbiology, shedding light on the long-awaited identification of the enzyme and the microbes behind its production. A groundbreaking discovery has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention and significantly improve medical treatments.
Pee is Yellow, Why?
In the liver, red blood cells undergo breakdown, resulting in the production of bilirubin. Excessive levels of bilirubin can have severe consequences, potentially resulting in life-threatening conditions. A recent research paper has shed light on the regulation of bilirubin levels and the potential consequences when this regulation is disrupted.
- IRS Grants Extra Time for 2024 Taxes to Kentucky’s April Storm Survivors
- Fed’s June Meeting: Rate Cuts Not in the Cards: What’s Next?
- Deadline Alert: Michigan Schools Must Act Fast with Federal Stimulus Funds
- How to Access VA Dependent Education Benefits with a 100% Disability Rating
- Big News for SSDI: Social Security Might Add $600 to Payments
At moderate concentrations, bilirubin plays a crucial role as an antioxidant, offering potential health advantages. In some cases, high levels of bilirubin in the blood can have harmful effects, causing jaundice and, in severe situations, a condition called kernicterus, which can lead to neurological damage.
In response to the excess bilirubin issue, the body converts the majority of it into a less harmful substance. A newly identified enzyme, bilirubin reductase, has been found to play a crucial role in the body’s transformation of bilirubin into urobilinogen. Researchers have discovered that a crucial gene is produced by a specific type of gut-dwelling bacteria called Firmicutes. This gene is responsible for bilirubin reductase.
Yellow Pee: The Sign of Good Health
A recent study has found a potential link between the absence of a specific gene responsible for producing yellow urine and an increased susceptibility to certain digestive diseases.
In a recent study on human gut metagenomes, researchers have discovered that bilirubin reductase is a highly prevalent enzyme among healthy adults. This finding suggests a potential role for bilirubin reductase in maintaining gut health. According to recent findings, the gene was found to be less common among individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and infants, particularly during the initial months of life when they are more prone to developing jaundice.
In the gut, oxygen levels are low, creating a challenging environment for the bacteria residing there. This poses a problem for scientists who wish to study these bacteria in laboratory settings, as they struggle to survive and grow under high-oxygen conditions. A limited amount of data was available due to the fact that only a few bacterial species had been identified as capable of metabolizing bilirubin.
New Medical Treatments Option
Understanding the connection between elevated bilirubin levels and conditions like jaundice, bowel disease, and kidney dysfunction could potentially pave the way for innovative medical interventions. Researchers are investigating the role of healthy gut bacteria in regulating bilirubin levels, which may offer promising avenues for future treatments. According to Hill, the next course of action involves delving into the study of how gut microbes control bilirubin levels.
Researchers are planning to conduct observational human studies in order to gain a deeper understanding of how gut microbes can impact the concentration of bilirubin in circulation. A particular focus of our investigation is on premature infants, who face a higher risk of jaundice and have a lower presence of bilirubin-reducing microbes.


Leave a Reply